Role of cloud computing in iot has been one of the biggest technological breakthroughs of the past decade, changing the way businesses operate and interact with their customers. The Internet of Things (IoT) has also emerged as a game-changing technology that has the potential to transform various industries. But what happens when you combine the two? In this article, we will discuss the role of cloud computing in IoT and how it is revolutionizing the way we interact with our devices.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, which enables them to connect
and exchange data over the internet. The IoT has the potential to create smart homes, smart cities, and smart industries by allowing devices to communicate and share data with each other.
Role of Cloud Computing in IoT
Cloud computing plays a crucial role in IoT by providing the infrastructure and resources needed to store, analyze, and process the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices. The cloud is
essentially a network of servers that can be accessed over the internet, providing on-demand access to computing resources such as storage, processing power, and software applications.
The cloud provides several benefits to IoT applications, such as:
Scalability: IoT applications often generate a large amount of data, which can quickly overwhelm on- premises computing resources. Cloud computing allows businesses to scale up or down their computing resources as needed, ensuring that they have enough resources to handle the influx of data generated by IoT devices.
Cost-effectiveness: Cloud computing is cost-effective for IoT applications because businesses only pay for the resources they use. This eliminates the need for businesses to purchase and maintain
their own computing infrastructure, which can be expensive.
Security: The cloud provides enhanced security features that protect IoT devices and data from cyber threats. Cloud service providers typically have robust security measures in place, including firewalls,
encryption, and access controls, to ensure that IoT data is protected.
Reliability: Cloud computing is highly reliable, with service providers offering high uptime guarantees. This is critical for IoT applications that require 24/7 availability.
Examples of Cloud Computing in IoT
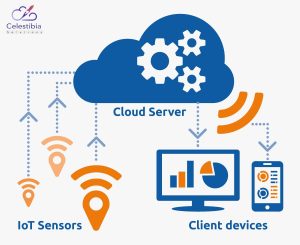
Smart Home Devices: Smart home devices such as thermostats, security cameras, and door locks are all examples of IoT devices that rely on cloud computing. These devices collect data and send it to
the cloud for processing and storage, enabling users to access the data remotely and control their devices from anywhere.
Industrial IoT: The industrial IoT (IIoT) is transforming industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and energy. In the manufacturing industry, IoT sensors are used to monitor
equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production. The data generated by these sensors is sent to the cloud for analysis and storage, enabling businesses to make data-
driven decisions and improve efficiency.
Wearable Devices: Wearable devices such as fitness trackers and smartwatches are also examples of IoT devices that rely on cloud computing. These devices collect data on users’ health and fitness and
send it to the cloud for processing and storage. This enables users to track their progress over time and access their data from any device.
Challenges of Cloud Computing in IoT
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits for IoT applications, there are also several challenges that businesses must address to ensure the success of their IoT initiatives.
Data Security: With the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, ensuring the security of that data is critical. Businesses must implement robust security measures to protect their data from cyber
threats.
Data Privacy: IoT devices collect personal data such as location, health information, and online behavior. Businesses must implement measures to protect user privacy and ensure that they are complying with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCP

